mirror of
https://github.com/qmk/qmk_firmware.git
synced 2025-08-25 16:25:26 +00:00
Compare commits
23 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
6274980e61 | ||
|
|
4083614023 | ||
|
|
3ba242cc3f | ||
|
|
b3853e7d40 | ||
|
|
d6184be67a | ||
|
|
519ce723fb | ||
|
|
6ae409dd55 | ||
|
|
fa2183a64a | ||
|
|
73883425a5 | ||
|
|
ef84bd9799 | ||
|
|
5eb69ca224 | ||
|
|
ba76fcfb8b | ||
|
|
945dd946ab | ||
|
|
94f58322ac | ||
|
|
a30dd2bb17 | ||
|
|
fc477a1ee7 | ||
|
|
f01a80968b | ||
|
|
3dec80b774 | ||
|
|
a5d22424f4 | ||
|
|
29dd664589 | ||
|
|
a91f439aec | ||
|
|
8f5ac39fb9 | ||
|
|
f8d8005835 |
@@ -79,6 +79,7 @@
|
||||
* [Hand Wiring Guide](hand_wire.md)
|
||||
* [ISP Flashing Guide](isp_flashing_guide.md)
|
||||
* [ARM Debugging Guide](arm_debugging.md)
|
||||
* [I2C Driver](i2c_driver.md)
|
||||
|
||||
* For a Deeper Understanding
|
||||
* [How Keyboards Work](how_keyboards_work.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,6 +79,7 @@
|
||||
* [Hand Wiring Guide](hand_wire.md)
|
||||
* [ISP Flashing Guide](isp_flashing_guide.md)
|
||||
* [ARM Debugging Guide](arm_debugging.md)
|
||||
* [I2C Driver](i2c_driver.md)
|
||||
|
||||
* For a Deeper Understanding
|
||||
* [How Keyboards Work](how_keyboards_work.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -122,6 +122,7 @@ The following options can be used to tweak the various animations:
|
||||
|`RGBLIGHT_EFFECT_KNIGHT_LED_NUM` |`RGBLED_NUM` |The number of LEDs to have the "Knight" animation travel |
|
||||
|`RGBLIGHT_EFFECT_CHRISTMAS_INTERVAL`|`1000` |How long to wait between light changes for the "Christmas" animation, in milliseconds|
|
||||
|`RGBLIGHT_EFFECT_CHRISTMAS_STEP` |`2` |The number of LEDs to group the red/green colors by for the "Christmas" animation |
|
||||
|`RGBLIGHT_RAINBOW_SWIRL_RANGE` |`360` |Range adjustment for the rainbow swirl effect to get different swirls |
|
||||
|
||||
You can also modify the speeds that the different modes animate at:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
83
docs/i2c_driver.md
Normal file
83
docs/i2c_driver.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
# I2C Master Driver
|
||||
|
||||
The I2C Master drivers used in QMK have a set of common functions to allow portability between MCUs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Available functions
|
||||
|
||||
|Function |Description |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
|`void i2c_init(void);` |Initializes the I2C driver. This function should be called once before any transaction is initiated. |
|
||||
|`uint8_t i2c_start(uint8_t address);` |Starts an I2C transaction. Address is the 7-bit slave address without the direction bit. |
|
||||
|`uint8_t i2c_transmit(uint8_t address, uint8_t* data, uint16_t length, uint16_t timeout);` |Transmit data over I2C. Address is the 7-bit slave address without the direction. |
|
||||
|`uint8_t i2c_transmit(uint8_t address, uint8_t* data, uint16_t length, uint16_t timeout);` |Transmit data over I2C. Address is the 7-bit slave address without the direction. Returns status of transaction. |
|
||||
|`uint8_t i2c_receive(uint8_t address, uint8_t* data, uint16_t length, uint16_t timeout);` |Receive data over I2C. Address is the 7-bit slave address without the direction. Saves number of bytes specified by `length` in `data` array. Returns status of transaction. |
|
||||
|`uint8_t i2c_writeReg(uint8_t devaddr, uint8_t regaddr, uint8_t* data, uint16_t length, uint16_t timeout);` |Same as the `i2c_transmit` function but `regaddr` sets where in the slave the data will be written. |
|
||||
|`uint8_t i2c_readReg(uint8_t devaddr, uint8_t regaddr, uint8_t* data, uint16_t length, uint16_t timeout);` |Same as the `i2c_receive` function but `regaddr` sets from where in the slave the data will be read. |
|
||||
|`uint8_t i2c_stop(uint16_t timeout);` |Stops the I2C driver. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Function Return
|
||||
|
||||
All the above functions, except `void i2c_init(void);` return the following truth table:
|
||||
|
||||
|Return Value |Description |
|
||||
|---------------|---------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
|0 |Operation executed successfully. |
|
||||
|-1 |Operation failed. |
|
||||
|-2 |Operation timed out. |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AVR
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
The following defines can be used to configure the I2C master driver.
|
||||
|
||||
|Variable |Description |Default|
|
||||
|------------------|---------------------------------------------------|-------|
|
||||
|`#F_SCL` |Clock frequency in Hz |400KHz |
|
||||
|`#Prescaler` |Divides master clock to aid in I2C clock selection |1 |
|
||||
|
||||
AVRs usually have set GPIO which turn into I2C pins, therefore no further configuration is required.
|
||||
|
||||
## ARM
|
||||
|
||||
For ARM the Chibios I2C HAL driver is under the hood.
|
||||
This section assumes an STM32 MCU.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration for ARM MCUs can be quite complex as often there are multiple I2C drivers which can be assigned to a variety of ports.
|
||||
|
||||
Firstly the `mcuconf.h` file must be setup to enable the necessary hardware drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
|Variable |Description |Default|
|
||||
|------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------|
|
||||
|`#STM32_I2C_USE_XXX` |Enable/Disable the hardware driver XXX (each driver should be explicitly listed) |FALSE |
|
||||
|`#STM32_I2C_BUSY_TIMEOUT` |Time in ms until the I2C command is aborted if no response is received |50 |
|
||||
|`#STM32_I2C_XXX_IRQ_PRIORITY` |Interrupt priority for hardware driver XXX (THIS IS AN EXPERT SETTING) |10 |
|
||||
|`#STM32_I2C_USE_DMA` |Enable/Disable the ability of the MCU to offload the data transfer to the DMA unit |TRUE |
|
||||
|`#STM32_I2C_XXX_DMA_PRIORITY` |Priority of DMA unit for hardware driver XXX (THIS IS AN EXPERT SETTING) |1 |
|
||||
|
||||
Secondly, in the `halconf.h` file, `#define HAL_USE_I2C` must be set to `TRUE`. This allows ChibiOS to load its I2C driver.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, we need to assign the correct GPIO pins depending on the I2C hardware driver we want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
By default the I2C1 hardware driver is assumed to be used. If another hardware driver is used, `#define I2C_DRIVER I2CDX` should be added to the `config.h` file with X being the number of hardware driver used. For example is I2C3 is enabled, the `config.h` file should contain `#define I2C_DRIVER I2CD3`. This aligns the QMK I2C driver with the Chibios I2C driver.
|
||||
|
||||
STM32 MCUs allows a variety of pins to be configured as I2C pins depending on the hardware driver used. By default B6 and B7 are set to I2C.
|
||||
|
||||
This can be changed by declaring the `i2c_init` function which intentionally has a weak attribute. Please consult the datasheet of your MCU for the available GPIO configurations. The following is an example initialization function:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
void i2c_init(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
setPinInput(B6); // Try releasing special pins for a short time
|
||||
setPinInput(B7);
|
||||
chThdSleepMilliseconds(10); // Wait for the release to happen
|
||||
|
||||
palSetPadMode(GPIOB, 6, PAL_MODE_ALTERNATE(4) | PAL_STM32_OTYPE_OPENDRAIN | PAL_STM32_PUPDR_PULLUP); // Set B6 to I2C function
|
||||
palSetPadMode(GPIOB, 7, PAL_MODE_ALTERNATE(4) | PAL_STM32_OTYPE_OPENDRAIN | PAL_STM32_PUPDR_PULLUP); // Set B7 to I2C function
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,99 +1,97 @@
|
||||
# Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Your computer keyboard has a processor inside of it, not unlike the one inside your computer. This processor runs software that is responsible for detecting button presses and sending reports about the state of the keyboard when they are pressed or released. QMK fills the role of that software, detecting button presses and passing that information on to the host computer. When you build your custom layout you are creating the equivalent of an .exe for your keyboard.
|
||||
Your computer keyboard has a processor inside of it, not unlike the one inside your computer. This processor runs software that is responsible for detecting button presses and sending reports about the state of the keyboard when buttons are pressed or released. QMK fills the role of that software, detecting button presses and passing that information on to the host computer. When you build your custom keymap, you are creating the equivalent of an executable program for your keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
QMK tries to put a lot of power into your hands by making easy things easy, and hard things possible. You don't have to know how to program to create powerful layouts, you only have to follow a few simple syntax rules.
|
||||
QMK tries to put a lot of power into your hands by making easy things easy, and hard things possible. You don't have to know how to program to create powerful keymaps — you only have to follow a few simple syntax rules.
|
||||
|
||||
# Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
Before you can build keymaps you need to install some software and setup your build environment. This only has to be done one time no matter how many keyboards you want to compile firmware for.
|
||||
Before you can build keymaps, you need to install some software and set up your build environment. This only has to be done once no matter how many keyboards you plan to compile firmware for.
|
||||
|
||||
## Download Software
|
||||
|
||||
### Text Editor
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need a program that can edit and save **plain text** files. If you are on Windows you can make due with Notepad, and on Linux you can use Gedit, both of which are simple but functional text editors. On macOS be careful with TextEdit.app, it will not save plain text files unless you make sure to select "Make Plain text" from the "Format" menu, or you can use another program such as Sublime Text.
|
||||
You'll need a program that can edit and save **plain text** files. If you're on Windows you can make do with Notepad, and on Linux you can use gedit. Both of these are simple but functional text editors. On macOS, be careful with the default TextEdit app: it will not save plain text files unless you explicitly select _Make Plain Text_ from the _Format_ menu.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also download and install a dedicated text editor like [Sublime Text](https://www.sublimetext.com/) or [VS Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/). This is probably the best way to go regardless of platform, as these programs are specifically made for editing code.
|
||||
|
||||
?> Not sure which text editor to use? Laurence Bradford wrote [a great introduction](https://learntocodewith.me/programming/basics/text-editors/) to the subject.
|
||||
|
||||
### QMK Toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
QMK Toolbox is an optional graphical Windows and macOS program that allows you to both program and debug your custom keyboard. You will likely prefer it to easily flash your keyboard and receive the debugging messages that your keyboard will print.
|
||||
QMK Toolbox is an optional graphical program for Windows and macOS that allows you to both program and debug your custom keyboard. You will likely find it invaluable for easily flashing your keyboard and viewing debug messages that it prints.
|
||||
|
||||
Download the files from the links below:
|
||||
[Download the latest release here.](https://github.com/qmk/qmk_toolbox/releases/latest)
|
||||
|
||||
For Windows: "qmk_toolbox.exe" or "qmk_toolbox_install.exe" (with installer)
|
||||
* For Windows: `qmk_toolbox.exe` (portable) or `qmk_toolbox_install.exe` (installer)
|
||||
* For macOS: `QMK.Toolbox.app.zip` (portable) or `QMK.Toolbox.pkg` (installer)
|
||||
|
||||
For Mac: "QMK.Toolbox.app.zip" or "QMK.Toolbox.pkg" (with installer)
|
||||
## Set Up Your Environment
|
||||
|
||||
* [Newest Release](https://github.com/qmk/qmk_toolbox/releases/latest)
|
||||
* [Source Code](https://github.com/qmk/qmk_toolbox/)
|
||||
We've tried to make QMK as easy to set up as possible. You only have to prepare your Linux or Unix environment, then let QMK install the rest.
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment Setup
|
||||
|
||||
We've tried to make QMK as easy to setup as possible. You only have to prepare your Linux or Unix environment and let QMK install the rest.
|
||||
|
||||
?> If you haven't worked with the Linux/Unix command line before there are a few basic concepts and commands you should learn. These resources will teach you enough to work with QMK:<br>
|
||||
?> If you haven't worked with the Linux/Unix command line before, there are a few basic concepts and commands you should learn. These resources will teach you enough to be able to work with QMK:<br>
|
||||
[Must Know Linux Commands](https://www.guru99.com/must-know-linux-commands.html)<br>
|
||||
[Some Basic Unix Commands](https://www.tjhsst.edu/~dhyatt/superap/unixcmd.html)
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to install msys2 and git.
|
||||
You will need to install MSYS2 and Git.
|
||||
|
||||
* Follow the installation instructions on the msys2 homepage: http://www.msys2.org
|
||||
* Close any open msys2 terminals, and open a new terminal
|
||||
* Install git by running this command: `pacman -S git`
|
||||
* Follow the installation instructions on the [MSYS2 homepage](http://www.msys2.org).
|
||||
* Close any open MSYS2 terminals and open a new MSYS2 MinGW 64-bit terminal.
|
||||
* Install Git by running this command: `pacman -S git`.
|
||||
|
||||
### macOS
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to install homebrew. Follow the instructions on the homebrew homepage: https://brew.sh
|
||||
You will need to install Homebrew. Follow the instructions on the [Homebrew homepage](https://brew.sh).
|
||||
|
||||
After homebrew is installed continue with "Download QMK", following step "Setup QMK" runs a script that will install other packages.
|
||||
After Homebrew is installed, continue with _Set Up QMK_. In that step you will run a script that will install other packages.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to install git. It's extremely likely you already have it, but if not one of the following commands should install it:
|
||||
You will need to install Git. It's very likely that you already have it, but if not, one of the following commands should install it:
|
||||
|
||||
* Debian/Ubuntu/Devuan: `apt-get install git`
|
||||
* Fedora/Redhat/Centos: `yum install git`
|
||||
* Debian / Ubuntu / Devuan: `apt-get install git`
|
||||
* Fedora / Red Hat / CentOS: `yum install git`
|
||||
* Arch: `pacman -S git`
|
||||
|
||||
## Download QMK
|
||||
?> Docker is also an option on all platforms. [Click here for details.](getting_started_build_tools.md#docker)
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have setup your Linux/Unix environment you are ready to download QMK. We will do this by using git to "clone" the QMK repository. Open a Terminal or MSYS2 Console window and leave it open for the remainder of this guide. Inside that window run these two commands:
|
||||
## Set Up QMK
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have set up your Linux/Unix environment, you are ready to download QMK. We will do this by using Git to "clone" the QMK repository. Open a Terminal or MSYS2 MinGW window and leave it open for the remainder of this guide. Inside that window run these two commands:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/qmk/qmk_firmware.git
|
||||
cd qmk_firmware
|
||||
|
||||
?> If you already know [how to use GitHub](getting_started_github.md) we recommend you create and clone your own fork instead. If you don't know what that means you can safely ignore this message.
|
||||
?> If you already know [how to use GitHub](getting_started_github.md), we recommend that you create and clone your own fork instead. If you don't know what that means, you can safely ignore this message.
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup QMK
|
||||
QMK comes with a script to help you set up the rest of what you'll need. You should run it now by typing in this command:
|
||||
|
||||
QMK comes with a script to help you setup the rest of what you'll need. You should run it now by typing in this command:
|
||||
|
||||
./util/qmk_install.sh
|
||||
util/qmk_install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
## Test Your Build Environment
|
||||
|
||||
Now that your QMK build environment is setup you can build a firmware for your keyboard. Start by trying to build the default layout for your keyboard. You should be able to do that with a command in this format:
|
||||
Now that your QMK build environment is set up, you can build a firmware for your keyboard. Start by trying to build the keyboard's default keymap. You should be able to do that with a command in this format:
|
||||
|
||||
make <keyboard>:default
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to build a firmware for a Clueboard 66% use:
|
||||
For example, to build a firmware for a Clueboard 66% you would use:
|
||||
|
||||
make clueboard/66/rev3:default
|
||||
|
||||
When it is done you should have a lot of output that ends similar to this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Linking: .build/clueboard_66_rev2_default.elf [OK]
|
||||
Creating load file for flashing: .build/clueboard_66_rev2_default.hex [OK]
|
||||
Copying clueboard_66_rev2_default.hex to qmk_firmware folder [OK]
|
||||
Checking file size of clueboard_66_rev2_default.hex [OK]
|
||||
* File size is fine - 25174/28672
|
||||
Linking: .build/clueboard_66_rev3_default.elf [OK]
|
||||
Creating load file for flashing: .build/clueboard_66_rev3_default.hex [OK]
|
||||
Copying clueboard_66_rev3_default.hex to qmk_firmware folder [OK]
|
||||
Checking file size of clueboard_66_rev3_default.hex [OK]
|
||||
* The firmware size is fine - 26356/28672 (2316 bytes free)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating Your Layout
|
||||
# Creating Your Keymap
|
||||
|
||||
Now you are ready to create your own personal layout. Move on to [Building Your First Firmware](newbs_building_firmware.md) for that.
|
||||
You are now ready to create your own personal keymap! Move on to [Building Your First Firmware](newbs_building_firmware.md) for that.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,6 +26,7 @@
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "i2c_master.h"
|
||||
#include "quantum.h"
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <hal.h>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,9 +42,11 @@ static const I2CConfig i2cconfig = {
|
||||
0
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
__attribute__ ((weak))
|
||||
void i2c_init(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
palSetGroupMode(GPIOB, GPIOB_PIN6 | GPIOB_PIN7, 0, PAL_MODE_INPUT); // Try releasing special pins for a short time
|
||||
setPinInput(B6); // Try releasing special pins for a short time
|
||||
setPinInput(B7);
|
||||
chThdSleepMilliseconds(10);
|
||||
|
||||
palSetPadMode(GPIOB, 6, PAL_MODE_ALTERNATE(4) | PAL_STM32_OTYPE_OPENDRAIN | PAL_STM32_PUPDR_PULLUP);
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||
/* Copyright 2018 MechMerlin
|
||||
* Copyright 2018 Logan Huskins
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||
/* Copyright 2018 MechMerlin
|
||||
* Copyright 2018 Logan Huskins
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
|
||||
@@ -17,28 +18,34 @@
|
||||
|
||||
const uint16_t PROGMEM keymaps[][MATRIX_ROWS][MATRIX_COLS] = {
|
||||
[0] = LAYOUT_60_ansi(
|
||||
KC_ESC, KC_1, KC_2, KC_3, KC_4, KC_5, KC_6, KC_7, KC_8, KC_9, KC_0, KC_MINS, KC_EQL, KC_BSPC,
|
||||
KC_TAB, KC_Q, KC_W, KC_E, KC_R, KC_T, KC_Y, KC_U, KC_I, KC_O, KC_P, KC_LBRC, KC_RBRC, KC_BSLS,
|
||||
MO(1), KC_A, KC_S, KC_D, KC_F, KC_G, KC_H, KC_J, KC_K, KC_L, KC_SCLN, KC_QUOT, KC_ENT,
|
||||
KC_LSFT, KC_Z, KC_X, KC_C, KC_V, KC_B, KC_N, KC_M, KC_COMM, KC_DOT, KC_SLSH, KC_LSFT,
|
||||
KC_LCTL, KC_LGUI, KC_LALT, KC_SPC, KC_RALT, MO(2), KC_RGUI, KC_RCTL),
|
||||
KC_ESC, KC_1, KC_2, KC_3, KC_4, KC_5, KC_6, KC_7, KC_8, KC_9, KC_0, KC_MINS,
|
||||
KC_EQL, KC_BSPC, KC_TAB, KC_Q, KC_W, KC_E, KC_R, KC_T, KC_Y, KC_U, KC_I, KC_O,
|
||||
KC_P, KC_LBRC, KC_RBRC, KC_BSLS, KC_CAPS, KC_A, KC_S, KC_D, KC_F, KC_G, KC_H,
|
||||
KC_J, KC_K, KC_L, KC_SCLN, KC_QUOT, KC_ENT, KC_LSFT, KC_Z, KC_X, KC_C, KC_V, KC_B,
|
||||
KC_N, KC_M, KC_COMM, KC_DOT, KC_SLSH, KC_RSFT, KC_LCTL, KC_LGUI, KC_LALT, KC_SPC,
|
||||
KC_RALT, KC_RGUI, MO(1), KC_LCTL
|
||||
),
|
||||
|
||||
[1] = LAYOUT_60_ansi(
|
||||
KC_GRV, KC_F1, KC_F2, KC_F3, KC_F4, KC_F5, KC_F6, KC_F7, KC_F8, KC_F9, KC_F10, KC_F11, KC_F12, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_UP, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_LEFT, KC_DOWN, KC_RGHT, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_LSFT, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS),
|
||||
[1] = LAYOUT_60_ansi(
|
||||
KC_GRV, KC_F1, KC_F2, KC_F3, KC_F4, KC_F5, KC_F6, KC_F7, KC_F8, KC_F9, KC_F10,
|
||||
KC_F11, KC_F12, KC_DEL, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_UP, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_PSCR, KC_SLCK, KC_PAUS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_LEFT, KC_DOWN,
|
||||
KC_RGHT, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_INS, KC_HOME, KC_PGUP, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_VOLU, KC_VOLD, KC_MUTE, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_END,
|
||||
KC_PGDN, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, MO(2), KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS
|
||||
),
|
||||
|
||||
[2] = LAYOUT_60_ansi(
|
||||
RESET, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_CAPS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, BL_STEP, BL_DEC, BL_INC, BL_TOGG, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, RGB_VAD, RGB_VAI, RGB_SAI, RGB_HUD, RGB_HUI, RGB_MOD, RGB_TOG, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS),
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, RESET, BL_TOGG, BL_INC, BL_DEC, BL_STEP, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, RGB_TOG, RGB_MOD, RGB_HUI,
|
||||
RGB_SAI, RGB_VAI, RGB_SPI, RGB_M_P, RGB_M_B, RGB_M_R, RGB_M_SW, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, RGB_RMOD, RGB_HUD, RGB_SAD, RGB_VAD, RGB_SPD, RGB_M_SN, RGB_M_K, RGB_M_X, RGB_M_G,
|
||||
KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS, KC_TRNS
|
||||
),
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
bool process_record_user(uint16_t keycode, keyrecord_t *record) {
|
||||
bool process_record_user(uint16_t keycode, keyrecord_t *record)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# 1up60hse default keymap
|
||||
# 1up60hse default keymap generated by QMK Configurator
|
||||
|
||||
This is the default keymap provided by [1upkeyboards](https://www.1upkeyboards.com).
|
||||
This is the keymap used by [QMK Configurator](https://config.qmk.fm/#/1upkeyboards/1up60hse/LAYOUT_60_ansi) as default.
|
||||
|
||||
## Notes
|
||||
- Software reset key is located on `Esc` on the third layer.
|
||||
|
||||
1
keyboards/30wer/30wer.c
Normal file
1
keyboards/30wer/30wer.c
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
#include "30wer.h"
|
||||
14
keyboards/30wer/30wer.h
Normal file
14
keyboards/30wer/30wer.h
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include "quantum.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define LAYOUT( \
|
||||
k00, k01, k02, k03, k04, k05, k06, k07, k08, k09, k0a, k0b, k0c, \
|
||||
k10, k11, k12, k13, k14, k15, k16, k17, k18, k19, k1a, k1b, k1c, \
|
||||
k20, k21, k22, k23, k24, k25, k26, k27, k28, k29, k2a, k2b \
|
||||
) \
|
||||
{ \
|
||||
{ k00, k01, k02, k03, k04, k05, k06, k07, k08, k09, k0a, k0b, k0c }, \
|
||||
{ k10, k11, k12, k13, k14, k15, k16, k17, k18, k19, k1a, k1b, k1c }, \
|
||||
{ k20, k21, k22, k23, k24, k25, k26, k27, k28, k29, k2a, k2b } \
|
||||
}
|
||||
31
keyboards/30wer/config.h
Normal file
31
keyboards/30wer/config.h
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include "config_common.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* USB Device descriptor parameter */
|
||||
#define VENDOR_ID 0x1234
|
||||
#define PRODUCT_ID 0x5678
|
||||
#define DEVICE_VER 0x0000
|
||||
#define MANUFACTURER 8o7wer
|
||||
#define PRODUCT 30wer
|
||||
#define DESCRIPTION Gherkin style construction 30% staggered pcb kit
|
||||
|
||||
/* key matrix size */
|
||||
#define MATRIX_ROWS 3
|
||||
#define MATRIX_COLS 13
|
||||
|
||||
/* pcb default pin-out */
|
||||
#define MATRIX_ROW_PINS { E6, B4, B5 }
|
||||
#define MATRIX_COL_PINS { F4, F5, F6, F7, B1, B3, B2, B6, D1, D0, D4, C6, D7 }
|
||||
#define UNUSED_PINS
|
||||
|
||||
/* COL2ROW or ROW2COL */
|
||||
#define DIODE_DIRECTION COL2ROW
|
||||
|
||||
/* key combination for command */
|
||||
#define IS_COMMAND() ( \
|
||||
keyboard_report->mods == (MOD_BIT(KC_LSHIFT) | MOD_BIT(KC_RSHIFT)) \
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
/* prevent stuck modifiers */
|
||||
#define PREVENT_STUCK_MODIFIERS
|
||||
51
keyboards/30wer/info.json
Normal file
51
keyboards/30wer/info.json
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"keyboard_name": "30wer",
|
||||
"url": "",
|
||||
"maintainer": "qmk",
|
||||
"width": 13.25,
|
||||
"height": 3,
|
||||
"layouts": {
|
||||
"LAYOUT": {
|
||||
"layout": [
|
||||
{"label":"Tab", "x":0, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"Q", "x":1, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"W", "x":2, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"E", "x":3, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"R", "x":4, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"T", "x":5, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"Y", "x":6, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"U", "x":7, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"I", "x":8, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"O", "x":9, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"P", "x":10, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"Bksp", "x":11, "y":0},
|
||||
{"label":"Delete", "x":12, "y":0, "w":1.25},
|
||||
{"label":"Ctrl", "x":0, "y":1, "w":1.25},
|
||||
{"label":"A", "x":1.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"S", "x":2.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"D", "x":3.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"F", "x":4.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"G", "x":5.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"H", "x":6.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"J", "x":7.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"K", "x":8.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"L", "x":9.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":":", "x":10.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"\"", "x":11.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"Enter", "x":12.25, "y":1},
|
||||
{"label":"Shift", "x":0, "y":2, "w":1.75},
|
||||
{"label":"Z", "x":1.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"X", "x":2.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"C", "x":3.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"V", "x":4.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"B", "x":5.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"N", "x":6.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"M", "x":7.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"<", "x":8.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":">", "x":9.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"?", "x":10.75, "y":2},
|
||||
{"label":"Space", "x":11.75, "y":2, "w":1.5}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
17
keyboards/30wer/keymaps/default/keymap.c
Normal file
17
keyboards/30wer/keymaps/default/keymap.c
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
#include QMK_KEYBOARD_H
|
||||
|
||||
const uint16_t PROGMEM keymaps[][MATRIX_ROWS][MATRIX_COLS] = {
|
||||
|
||||
[0] = LAYOUT( \
|
||||
KC_TAB, KC_Q, KC_W, KC_E, KC_R, KC_T, KC_Y, KC_U, KC_I, KC_O, KC_P, KC_LBRC, KC_BSPC, \
|
||||
KC_LCTL, KC_A, KC_S, KC_D, KC_F, KC_G, KC_H, KC_J, KC_K, KC_L, KC_SCLN, KC_QUOT, KC_ENT, \
|
||||
KC_LSFT, KC_Z, KC_X, KC_C, KC_V, KC_B, KC_N, KC_M, KC_COMM, KC_DOT, KC_SLSH, LT(1, KC_SPC) \
|
||||
),
|
||||
|
||||
[1] = LAYOUT( \
|
||||
KC_ESC, KC_1, KC_2, KC_3, KC_4, KC_5, KC_6, KC_7, KC_8, KC_9, KC_0, KC_UP, KC_DEL, \
|
||||
_______, _______, _______, _______, RESET, _______, _______, _______, _______, _______, KC_LEFT, KC_RGHT, _______, \
|
||||
KC_LALT, _______, _______, _______, _______, _______, _______, _______, _______, _______, KC_DOWN, _______ \
|
||||
),
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
16
keyboards/30wer/readme.md
Normal file
16
keyboards/30wer/readme.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
30wer by 8o7wer
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Keyboard Maintainer: [Filip Sund](https://github.com/FSund)
|
||||
Hardware Supported: Pro Micro
|
||||
Hardware Availability: Group buy
|
||||
|
||||
More info in the [group by thread at Keebtalk](https://www.keebtalk.com/t/gb-30wer-by-8o7wer/3618/).
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make 30wer:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
60
keyboards/30wer/rules.mk
Normal file
60
keyboards/30wer/rules.mk
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
# MCU name
|
||||
MCU = atmega32u4
|
||||
|
||||
# Processor frequency.
|
||||
# This will define a symbol, F_CPU, in all source code files equal to the
|
||||
# processor frequency in Hz. You can then use this symbol in your source code to
|
||||
# calculate timings. Do NOT tack on a 'UL' at the end, this will be done
|
||||
# automatically to create a 32-bit value in your source code.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This will be an integer division of F_USB below, as it is sourced by
|
||||
# F_USB after it has run through any CPU prescalers. Note that this value
|
||||
# does not *change* the processor frequency - it should merely be updated to
|
||||
# reflect the processor speed set externally so that the code can use accurate
|
||||
# software delays.
|
||||
F_CPU = 16000000
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# LUFA specific
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Target architecture (see library "Board Types" documentation).
|
||||
ARCH = AVR8
|
||||
|
||||
# Input clock frequency.
|
||||
# This will define a symbol, F_USB, in all source code files equal to the
|
||||
# input clock frequency (before any prescaling is performed) in Hz. This value may
|
||||
# differ from F_CPU if prescaling is used on the latter, and is required as the
|
||||
# raw input clock is fed directly to the PLL sections of the AVR for high speed
|
||||
# clock generation for the USB and other AVR subsections. Do NOT tack on a 'UL'
|
||||
# at the end, this will be done automatically to create a 32-bit value in your
|
||||
# source code.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no clock division is performed on the input clock inside the AVR (via the
|
||||
# CPU clock adjust registers or the clock division fuses), this will be equal to F_CPU.
|
||||
F_USB = $(F_CPU)
|
||||
|
||||
# Interrupt driven control endpoint task(+60)
|
||||
OPT_DEFS += -DINTERRUPT_CONTROL_ENDPOINT
|
||||
|
||||
# Bootloader
|
||||
# This definition is optional, and if your keyboard supports multiple bootloaders of
|
||||
# different sizes, comment this out, and the correct address will be loaded
|
||||
# automatically (+60). See bootloader.mk for all options.
|
||||
BOOTLOADER = caterina
|
||||
|
||||
# Build Options
|
||||
# change to "no" to disable the options, or define them in the Makefile in
|
||||
# the appropriate keymap folder that will get included automatically
|
||||
#
|
||||
BOOTMAGIC_ENABLE = no # Virtual DIP switch configuration(+1000)
|
||||
MOUSEKEY_ENABLE = no # Mouse keys(+4700)
|
||||
EXTRAKEY_ENABLE = yes # Audio control and System control(+450)
|
||||
CONSOLE_ENABLE = yes # Console for debug(+400)
|
||||
COMMAND_ENABLE = no # Commands for debug and configuration
|
||||
NKRO_ENABLE = yes # Nkey Rollover - if this doesn't work, see here: https://github.com/tmk/tmk_keyboard/wiki/FAQ#nkro-doesnt-work
|
||||
BACKLIGHT_ENABLE = no # Enable keyboard backlight functionality
|
||||
MIDI_ENABLE = no # MIDI controls
|
||||
AUDIO_ENABLE = no # Audio output
|
||||
UNICODE_ENABLE = no # Unicode
|
||||
BLUETOOTH_ENABLE = no # Enable Bluetooth with the Adafruit EZ-Key HID
|
||||
RGBLIGHT_ENABLE = no # Enable WS2812 RGB underlight.
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,8 @@ Hardware Availability: [4x4x4x4x4 project on 40% Keyboards](http://www.40percent
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make 4x4:default
|
||||
make 40percentclub/4x4:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
|
||||
See [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/build_environment_setup.html) then the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/make_instructions.html) for more information.
|
||||
First pass at adding support for the 4x4 keyboard. Compiles but completely untested. Intended to kick-start development.
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# MCU name
|
||||
#MCU = at90usb1286
|
||||
MCU = atmega32u4
|
||||
|
||||
# Processor frequency.
|
||||
@@ -43,11 +42,11 @@ OPT_DEFS += -DINTERRUPT_CONTROL_ENDPOINT
|
||||
# Atmel DFU loader 4096
|
||||
# LUFA bootloader 4096
|
||||
# USBaspLoader 2048
|
||||
OPT_DEFS += -DBOOTLOADER_SIZE=4096
|
||||
# OPT_DEFS += -DBOOTLOADER_SIZE=4096
|
||||
|
||||
# Bootloader
|
||||
# This definition is optional, and if your keyboard supports multiple bootloaders of
|
||||
# different sizes, comment this out, and the correct address will be loaded
|
||||
# different sizes, comment this out, and the correct address will be loaded
|
||||
# automatically (+60). See bootloader.mk for all options.
|
||||
BOOTLOADER = caterina
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,4 +70,5 @@ AUDIO_ENABLE = no # Audio output on port C6
|
||||
FAUXCLICKY_ENABLE = no # Use buzzer to emulate clicky switches
|
||||
HD44780_ENABLE = no # Enable support for HD44780 based LCDs (+400)
|
||||
|
||||
LAYOUTS = ortho_4x4 ortho_4x8 ortho_4x12 ortho_4x16
|
||||
#FIXME: Community keymap build are currently failing due to missing functionality
|
||||
#LAYOUTS = ortho_4x4 ortho_4x8 ortho_4x12 ortho_4x16
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,8 @@ Hardware Availability: [5x5 project on 40% Keyboards](http://www.40percent.club/
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make 5x5:default
|
||||
make 40percentclub/5x5:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
|
||||
See [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/build_environment_setup.html) then the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/make_instructions.html) for more information.
|
||||
First pass at adding support for the 4x4 keyboard. Compiles but completely untested. Intended to kick-start development.
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# MCU name
|
||||
#MCU = at90usb1286
|
||||
MCU = atmega32u4
|
||||
|
||||
# Processor frequency.
|
||||
@@ -43,7 +42,7 @@ OPT_DEFS += -DINTERRUPT_CONTROL_ENDPOINT
|
||||
# Atmel DFU loader 4096
|
||||
# LUFA bootloader 4096
|
||||
# USBaspLoader 2048
|
||||
OPT_DEFS += -DBOOTLOADER_SIZE=4096
|
||||
# OPT_DEFS += -DBOOTLOADER_SIZE=4096
|
||||
|
||||
# Bootloader
|
||||
# This definition is optional, and if your keyboard supports multiple bootloaders of
|
||||
@@ -71,4 +70,5 @@ AUDIO_ENABLE = no # Audio output on port C6
|
||||
FAUXCLICKY_ENABLE = no # Use buzzer to emulate clicky switches
|
||||
HD44780_ENABLE = no # Enable support for HD44780 based LCDs (+400)
|
||||
|
||||
LAYOUTS = ortho_5x5 ortho_5x10 ortho_5x15
|
||||
#FIXME: Community keymap build are currently failing due to missing functionality
|
||||
#LAYOUTS = ortho_5x5 ortho_5x10 ortho_5x15
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# 6lit
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
6 key macropad that fits within the 100mm x 100mm PCB size. Can be used singly as a regular 6 key macropad as well.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,6 +13,6 @@ Hardware Availability: [6lit project on 40% Keyboards](http://www.40percent.club
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make 6lit:default
|
||||
make 40percentclub/6lit:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# foobar
|
||||
|
||||
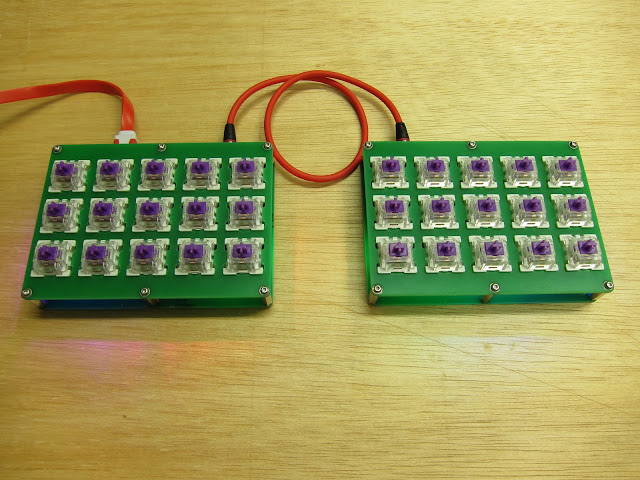
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
Split 30% keyboard that fits within the 100mm x 100mm PCB size. Can be used together as a split keyboard or as a single 15 key macropad.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,6 +13,6 @@ Hardware Availability: [foobar project on 40% Keyboards](http://www.40percent.cl
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make foobar:default
|
||||
make 40percentclub/foobar:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Gherkin
|
||||
# Gherkin
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
A 30 key keyboard.
|
||||
@@ -11,8 +13,9 @@ Hardware Availability: [Gherkin project on 40% Keyboards](http://www.40percent.c
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make gherkin:default
|
||||
make 40percentclub/gherkin:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
|
||||
See [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/build_environment_setup.html) then the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/make_instructions.html) for more information.
|
||||
First pass at adding support for the gherkin keyboard. Compiles but completely
|
||||
untested. Intended to kick-start development.
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,8 @@
|
||||
# Luddite
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
Luddite 60% keyboard with backlight and RGB underglow.
|
||||
|
||||
* [The original TMK firmware](https://github.com/di0ib/tmk_keyboard/tree/master/keyboard/luddite)
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +13,7 @@ Hardware Availability: [Luddite project on 40% Keyboards](http://www.40percent.c
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make luddite:default
|
||||
make 40percentclub/luddite:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
|
||||
18
keyboards/40percentclub/mf68/readme.md
Normal file
18
keyboards/40percentclub/mf68/readme.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
# mf68
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
Magicforce 68 with [replacement PCB](https://github.com/di0ib/tmk_keyboard/tree/master/keyboard/mf68) designed by [di0ib](https://github.com/di0ib).
|
||||
|
||||
* [The original TMK firmware](https://github.com/di0ib/tmk_keyboard/tree/master/keyboard/mf68)
|
||||
|
||||
Keyboard Maintainer: QMK Community
|
||||
Hardware Supported: Pro Micro
|
||||
Hardware Availability: [PCB files](https://github.com/di0ib/tmk_keyboard/tree/master/keyboard/mf68/pcb)
|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make 40percentclub/mf68:default
|
||||
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
@@ -1,10 +1,12 @@
|
||||
MF68
|
||||
====
|
||||
# mf68_ble
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
Magicforce 68 with [replacement PCB](https://github.com/di0ib/tmk_keyboard/tree/master/keyboard/mf68) designed by [di0ib](https://github.com/di0ib).
|
||||
|
||||
Keyboard Maintainer: [di0ib](http://www.40percent.club)
|
||||
Hardware Supported: [Feather 32u4 Bluefruit](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-feather-32u4-bluefruit-le/)
|
||||
Keyboard Maintainer: QMK Community
|
||||
Hardware Supported: [Feather 32u4 Bluefruit](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-feather-32u4-bluefruit-le/)
|
||||
Please note: This is 32u4 and not M0
|
||||
Hardware Availability: [PCB files](https://github.com/di0ib/tmk_keyboard/tree/master/keyboard/mf68/pcb)
|
||||
[MF68 thicc case files](https://github.com/harshitgoel96/mf68-case-thicc)
|
||||
@@ -20,8 +22,8 @@ Below is how you wire the Feather to PCB
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
Make example for this keyboard (after setting up your build environment):
|
||||
|
||||
make mf68_ble:default
|
||||
make 40percentclub/mf68_ble:default
|
||||
|
||||
See [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/build_environment_setup.html) then the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/make_instructions.html) for more information.
|
||||
See the [build environment setup](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_build_tools) and the [make instructions](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/getting_started_make_guide) for more information. Brand new to QMK? Start with our [Complete Newbs Guide](https://docs.qmk.fm/#/newbs).
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user